Have you ever wondered that the current lithium battery technology has reached its limit? And for future technological solutions it is not enough. In this article, we will talk about what will replace it in the near future, namely graphene.
Lithium-ion battery, although it is now the most common, has many disadvantages:
Nobody wondered why Apple doesn't put chargers over 5 watts in their smartphones? And because the faster the battery charges, the more it will heat up. Namely, high temperatures reduce the cycles and the volume of the battery.
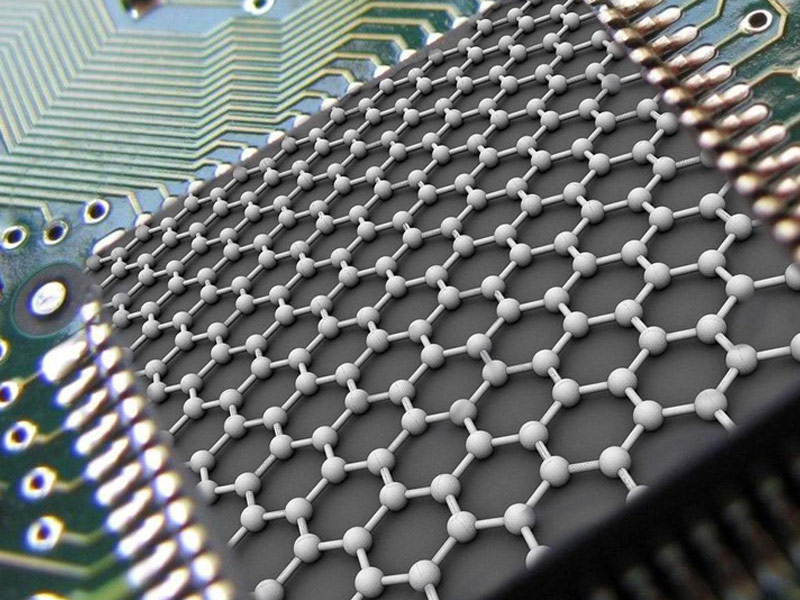
Graphene is one of the allotropic forms of carbon, a monoatomic layer of carbon atoms with a hexagonal structure. Graphene was discovered in 2004 by Andriy Geim and Konstantin Novoselov from the University of Manchester. For this discovery, Game and Novoselov were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010.
Back in the late 1980s, Volodymyr Lytovchenko, a corresponding member of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, and his staff (V. Lashkarev Institute of Semiconductor Physics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine) studied the appearance of a forbidden zone in deformed ultra-thin graphite films (which are now considered multilayer graphene).
Just imagine an incredibly light atom-thick plate that is 200 times stronger than steel. The amazing properties of graphene are not limited to this. It can also be flexible, transparent, and its electrical conductivity exceeds the electrical conductivity of copper. & Nbsp; In simple words, graphene is a carbon film with a thickness of 1 atom, which is made of the same material as ordinary graphite pencils. If you add 3 million sheets of graphene, you can get a thickness of about 1 mm.
Some products containing graphene elements are already on the market today. For example, well-known headphones use graphene membranes. The developers claim that such membranes perfectly transmit small details of sound.
In November 2017, Samsung Electronics announced the development of new batteries for smartphones that can be charged in just 12 minutes, as opposed to conventional ones, which charge in about an hour or two. & nbsp; Samsung is doing research to improve graphene production, which will lead to miniature electronics. The company's specialists are working on creating mobile phones the size of a bank plastic card. Graphene can replace the silicon used in the manufacture of chips.
Currently, & nbsp; indium tin oxide (ITO) is used to produce transparent touch screens. But this material has a drawback - it is very fragile. Graphene does not have this disadvantage.
Graphene-based
has already created supersensitive sensors (can detect the presence of a single electron), biosensors, high-capacity miniature capacitors, high-speed non-volatile memory elements, radiation modulators, transparent touch screens with a diagonal of more than 80 & nbsp; cm. IBM has developed graphene-based field-effect transistors with a speed of 100 GHz.
Basically, the developments of scientists are aimed at creating large batteries for transport. Car mileage on a single charge of the Tesla Model S is 800-1000 km, charging speed is 10-12 minutes.
Production of graphene batteries is promising. It is such a capacious and fast-charging source of energy is not enough for the development of electric vehicles. It is also important that the new battery weighs 2 times less than lithium-ion batteries. Its mechanical properties fit perfectly into the operating conditions of the machines. Graphene is 200 times stronger than steel, elastic. The first prototypes are already being tested.
The disadvantage of grafen is that it is very difficult to produce. Until now, scientists have managed to make it only in small quantities, the largest of which was a letter the size of a credit card. Until recently, they couldn't even make it outside the lab.
To make a graphene sheet the size of a credit card, soybean oil was heated to 800 ° C on a sheet of nickel foil, causing the carbon to settle into a thin plate of graphene. But it is still a problem of scaling. When trying to get large graphene sheets, the material was of low quality. However, this problem of the balance of purity and size of graphene materials is similar to the similar problem of obtaining pure silicon, which was in previous years.
Summarizing all the above and taking into account all the advantages and disadvantages of this material, we can say the only right thing - of course, graphene is the material of the near future, which will improve almost all electronic gadgets. Yes, lithium will still be at the top of the components for battery production in the coming years, but the time for new technology is almost here. And those innovations that will come to us with this new material will bring improvement to everyone. In addition, it has a less negative impact on the environment. After all, the well-known lithium, when improperly disposed of, harms our planet no less than oil or gas production, and it's time to change that.